Lyre music formed the basis for some of the earliest music in Africa. In lyre music, a bow is used to pluck one or more strings that are often attached to a resonator such as a gourd or basket lined with animal skin. The word lyre comes from the Latin word, lyrum, meaning “mantle” or “pouch” and thus had connotations of a hollow shape. Lyres were originally made from tortoiseshell and wood before evolving into more sophisticated materials such as metals, particularly precious metals.
In this article, I will talk about “African Musical Instruments”. Let’s start.
Culture Facts
African Musical Instruments
African music is a very broad term. It includes music from all over the continent, including North Africa. It also includes music that came to Africa via trade routes and colonization. The instruments used in African music tend to be very diverse, with many different types of drums, horns and flutes.
African musical instruments are usually made from wood or other organic materials. They are often decorated with animal skins or beads. Some instruments are even carved into the shape of animals for increased resonance when played!
Some common instruments include:
Drums: Drums are probably the most common type of instrument in Africa. They can be made out of almost anything that is hollow and has some resonance when hit with something hard! The most popular drums are made out of wood or metal with skins stretched over them to create a resonating sound when struck with a stick or mallet (an object used to strike at the head of an instrument).
Horn: Horns come in many different forms, but they all have one thing in common: they produce sound by vibrating rather than through blowing air into them like horns used in Western music do. African horns include trumpets, clarinets and flutes that use this principle to make their sounds!
Instruments Used In West African Music
African music is a very broad term that can include many different styles and types of music. The African continent is a huge area and the people who live there have developed many different musical traditions.
Instruments Used In West African Music
The most common instruments used in West African music include:
The kora is a 21 string harp-like instrument that is played by plucking or strumming. It’s used in Mali, Guinea, Senegal, Gambia and Burkina Faso.
The ngoni is a 3 stringed lute that comes from West Africa. It’s played by plucking the strings with one finger on each hand. It’s been around since at least the 14th century!
The balafon is a wooden Xylophone that comes from West Africa. It’s been around for over 2000 years!
In common with other African music traditions, West African music is based on a pentatonic scale. The oldest written music that has come down to us is that of the griots, who were court musicians in the Mandingo Empire of Mali. They were expected to have an extensive knowledge of history and genealogy.
Instruments Used In West African Music
Drums are very important in West African music, both for accompaniment and for solo parts. A wide variety of percussion instruments are used: drums, wooden blocks, rattles, bells and so on.
Gongs are also common in West African music; these may be mounted on stools or carried by hand. The most important gong is the kakaki (also known as kakakò) which is made from copper or brass. It has a distinctive sound that can be heard over great distances and it can carry a melody quite well on its own.

The Griots
The Griots
The Griots are the traditional storytellers and genealogists of West Africa. They are also known as jeli or djeli (in Mandinka), or gawlo in Songhay languages. The term may also be applied to a singer, poet or musician, or someone who knows many songs.
The Griots originated in the southern region of Senegal, but have migrated across West Africa over the centuries. They were traditionally responsible for recording events such as births, marriages and deaths in their communities by singing them aloud, which was considered more accurate than written records at the time. Today they are still often called upon to recite historical tales of their community during significant events such as weddings, funerals and births.[1]
Griots were also responsible for entertaining their communities with music and dance. Their role as historians has earned them the nickname ‘the memory of Africa’.
The Griots:
The griots are a group of musicians who play a variety of instruments, including the kora, balafon and ngoni. They are traditionally seen as the keepers of history and culture in West Africa.
In African culture, griots are considered to be among the most important people in the community. Their role is similar to that of a bard or oral historian in Europe or America. They are often hired by families to remember their history by singing praise songs about them at weddings and other celebrations.
Modern Musical Fusions
In the African diaspora, music has been fused with other genres. For instance, in Brazil and Cuba, African slaves were forced to play European instruments, such as the violin and guitar, and make them sound like their own traditional instruments.
In Brazil, this fusion resulted in Samba. In Cuba, it resulted in Rumba.
African music is a vast and rich collection of sounds, rhythms and instruments. It covers a wide range of styles, including traditional folk music and pop music as well as more modern fusion genres.
Most African countries have their own popular genres that are well known around the world. These include soukous from Congo, Highlife from Ghana and mbalax from Senegal.
The continent has also produced many popular pop stars, including Youssou Ndour of Senegal, King Sunny Adé of Nigeria, Salif Keita of Mali and Thomas Mapfumo of Zimbabwe.
African music is a rich, vibrant and diverse array of musical styles that have developed in Africa. It features complex rhythms, polyrhythms, percussion instruments and vocal styles using wide tonal ranges and different vocal techniques. The term “African music” encompasses different types of music including African popular music (including highlife, Afrobeat and pop), traditional music (including folk music, religious music and martial arts music) and contemporary classical music.
The continent’s diverse population has spawned many different kinds of music. In some cases, the accompanying dance may be called the dance-song or dance-drummer. Many African songs use call and response patterns (e.g., “Mbube” by Solomon Linda, 1951). A large number of African songs have been adapted for Western Classical Music.

Learning To Hear The Rhythms
Learning To Hear The Rhythms
Learning to hear and feel the rhythms is an important part of learning to play African instruments. This can be done by listening to music, drumming, dancing and clapping.
If you have a rhythm instrument at home, such as a drum or marimba, try making up simple rhythms on it. You might also like to sing along with some of the music that you are hearing on the radio or television. This will help you develop your sense of rhythm. You should also try moving your body in time with the music.
If you do not have an instrument at home, you could borrow one from a friend or relative and practise playing along with their music collection. If they don’t mind sharing theirs then even better!
Learning To Hear The Rhythms
This is the most important skill to develop when you are learning African music. It is a skill that will serve you well in all musical traditions.
Rhythm is the emotional and expressive heart of music. It is what makes people dance and sing along, whether they know what they are singing or not. Rhythm also gives us a sense of time, which is crucial to our survival as human beings. If we did not have some sense of where we were in time, we would not be able to coordinate our movements with those around us and thus could not survive as social animals.
Rhythm can be defined in two ways: as the pattern of accented notes (the rhythm) and as the energy created by playing these patterns (the groove).
FAQs for African Musical Instruments
Now that you understand “African Musical Instruments”, let’s move on to the FAQ section.
What Are The Four African Musical Instruments?
African Musical Instruments: Four Key Instruments
The four main instruments used in African music are the xylophone, drums, harp and flute. Each of these instruments has a unique sound and function within the musical ensemble.
Xylophone
The xylophone is one of the oldest musical instruments in Africa. The first xylophones were handcrafted out of wood or gourds and later made with metal keys. Typically, the xylophones are made from bamboo or calabash tree canes with metal keys or pegs attached to them. The instrument is played by striking the keys with mallets, sticks or fingers and produces a percussive sound similar to that of a piano or marimba.
Drums
Drums are one of the most basic forms of percussion instruments found worldwide and have been used for centuries by Africans in many traditional dances and ceremonies such as weddings, funerals and religious rituals. They come in all shapes and sizes but are usually round containers filled with dried seeds or sand that produces a hollow booming sound when struck with sticks or hands. Different types of drums vary according to their size, shape, material composition and how they are played (either by hand or foot).
What Are Ten African Instruments?
African instruments are a wide variety of musical instruments that originated in Africa. They include percussion instruments, string instruments and hornbosts. The following is a list of ten African musical instruments.
The Kora
The Kora is one of the most popular African instruments. It is a harp-like instrument that has 21 strings, each tuned to a different pitch. The instrument was invented by the Fula people around the 14th century A.D. The Kora is considered an important symbol of African culture and heritage.
The Bamana Ngoni
The Bamana Ngoni is another popular African instrument that comes from Mali in West Africa. It is similar in appearance to a violin but has only one string and has no fingerboard or frets on it at all! The performer plucks this string with his fingers or by tapping it with his bare hand to produce different notes and chords from it.
The African continent is a place of great diversity and rich culture. If you’ve ever been to Africa, then you know that the music is just as diverse as the people. But there are some instruments that are common in many African countries.
Instruments like the kora, mbira and djembe are well known outside of Africa as well. So if you’re looking for a musical instrument to add to your collection, these ten African instruments might be what you’re looking for!
What Is The Oldest African Instrument?
The oldest African instruments are the drums. The oldest drum is the “talking drums” which has been used for thousands of years in West Africa.
What Is The Oldest African Instrument?
The oldest African instrument is the talking drum, which is still used today in West Africa. The talking drum is a hollowed out log with a membrane stretched across one end and attached to the other end of the log by rope or leather thongs. The membrane can be made from goat skin, fish skin or even the skin of an elephant. A musician will strike the membrane with their hands or beat it with sticks to produce different sounds depending on how they strike it and how hard they hit it. Talking drums were used by warriors as well as hunters because they could communicate over long distances using them.
The Oldest African Instrument
The oldest African instrument is the stick-drum. It was developed in Africa and then migrated to Europe, where it became the snare drum.
The stick-drum consists of a frame made of wood or other material, with a thin membrane stretched over it. A player beats on the membrane with a stick or stick-like object. The sound produced is similar to that of the snare drum, which was developed later in Europe.
What Is The Main Instrument In Africa?
What Is The Main Instrument In Africa?
The main instrument of African music is the drum. The drum has been used for thousands of years, and is used in most songs and dances. It can be found throughout Africa, regardless of whether it is played by a man or woman.
The drums are made out of animal skins stretched across wooden frames, with various sizes and shapes depending on the region they come from. They can be played either by hand or with sticks, and are often accompanied by other percussion instruments such as rattles and bells.
The main instrument in Africa is the drum. The drum is made from animal skin, wood and cowhide. It is played by striking it with the hands, sticks and mallets.
Other instruments include the kora (a 21-stringed harp), balafon (a xylophone), ngoni (a banjo-like lute) and various types of horns and flutes.
The main instrument in Africa is the drum. It’s used in almost every musical genre, and it’s been around for thousands of years.
The drum is made from animal skins stretched over a hollowed-out log or gourd. You can play it with your hands or beat it with sticks.
African drums are very loud and make a lot of noise! They’re also very old. Archaeologists have found evidence that people were making drums thousands of years ago in Egypt, Africa and Asia.
What Are The 5 Classification Of Traditional African Instruments?
The African continent is rich in music and musical instruments. The traditional African instruments are classified into four main categories: membranophones, idiophones, chordophones and aerophones.
Membranophones
These are instruments that make sound by vibrating a flexible membrane. Examples of membranophones include drums, such as the talking drum, marimba and xylophone.
Idiophones
Idiophones produce sound by striking or shaking them. Examples include bells and gongs.
Chordophones
Chordophones produce sound by the vibration of strings when plucked or strummed. Strings can be made of various materials including metal wire or gut strings. Stringed instruments include harps, lyres and lutes.
Aerophones
Aerophones produce sound via vibrating air columns inside tubes such as flutes (transverse flute), panpipes (end-blown flute) and recorders (transverse flute).
One of the most important elements of African music is the use of drums. The drum is the most basic instrument, and it is used during ceremonies to celebrate life and death. Drums are also used to call people together for meetings, festivals, or religious ceremonies.
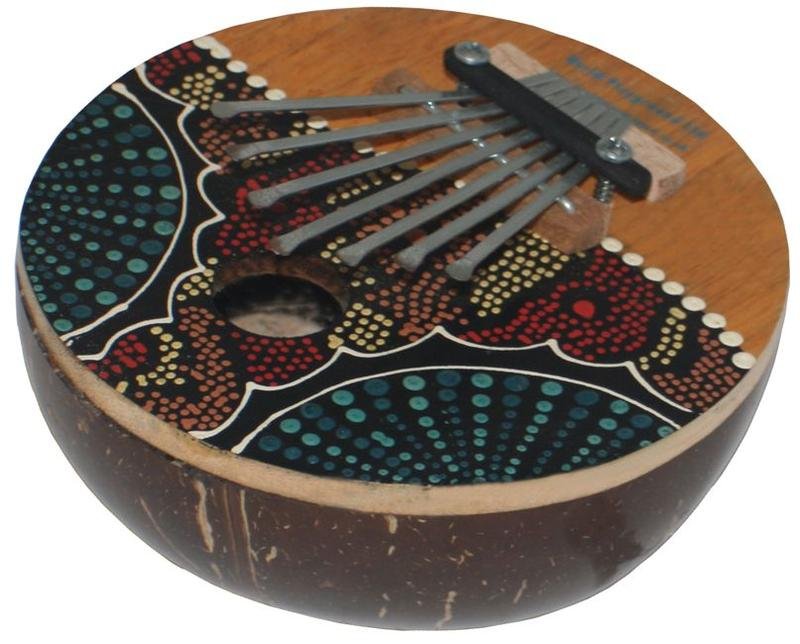
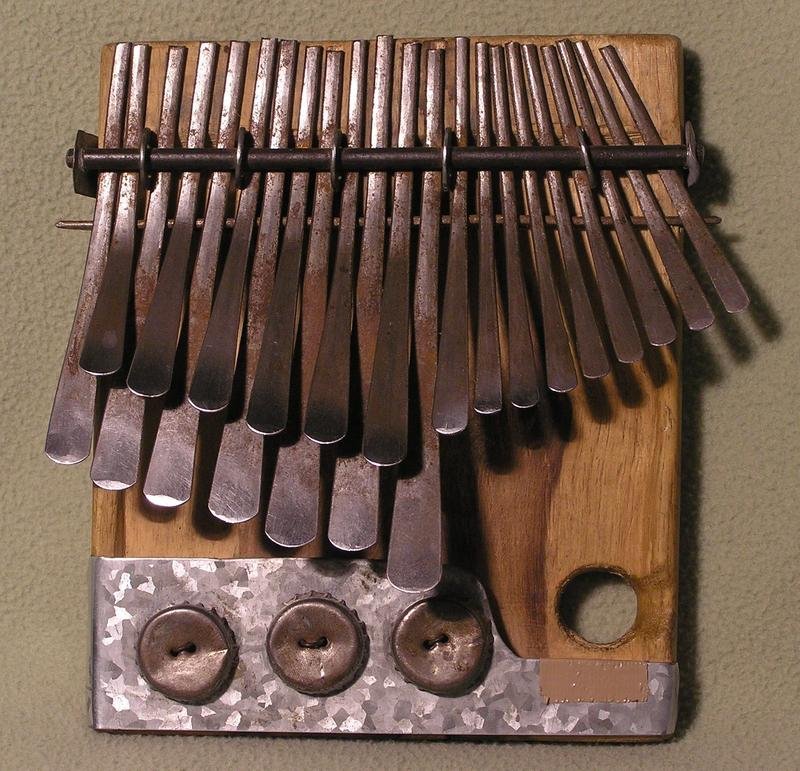
The first classification of traditional African instruments is the membranophones. These include drums and other instruments that use membranes. For example, a kalimba (also known as mbira) uses a wooden board with metal keys that are pressed down with the fingers to create tones. Another membranophone is the marimba, which consists of bars that are struck with mallets.
Conclusion for African Musical Instruments
As you can see, african musical instruments include a variety of drums, horns, and other types of percussion. We hope you enjoyed our list, and hope you will continue to listen to each one of these wonderful tunes. In future articles we’ll delve into more African instruments like the Kora and Xylophone.
Thank you for reading, and I hope you get the point of “African Musical Instruments”. If not, please contact me or leave a comment below. I would be pleased to help in any way I can.